Interfacing DHT22
Written By - Tanya Sharma
The DHT 22 ,is also known as AM2302finds numerous applications across various industries and fields due to its ability to measure temperature and humidity accurately. There are countless projects you can undertake using the DHT22 sensor due to its versatility in measuring temperature and humidity. Here are a few project ideas
Home Weather Station Indoor Climate Monitoring Plant Monitoring System HVAC Control Incubator Controller Food Storage Monitoring etc .
Overview of Dht22 Sensor And Arduino
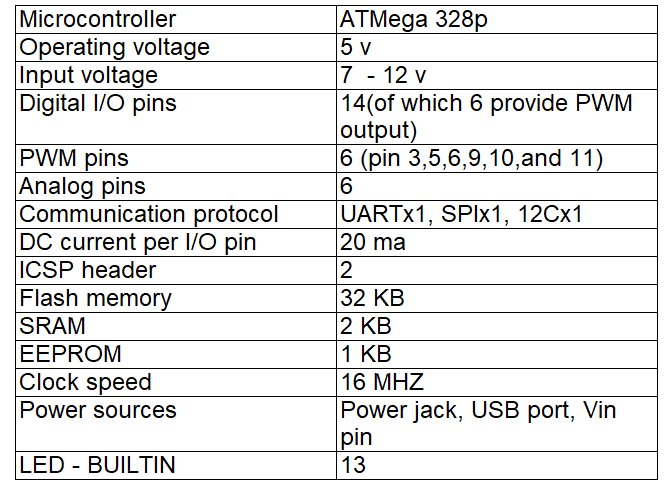
DHT 22 SENSOR : The DHT22 sensor is a popular digital sensor that is used to measure temperature and humidity. It is also known as the AM2302 sensor.Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based on easy-to-use hardware and software. Arduino boards are able to read inputs - light on a sensor, a finger on a button, or a Twitter message - and turn it into an output - activating a motor, turning on an LED, publishing something online. You can tell your board what to do by sending a set of instructions to the microcontroller on the board. To do so you use the Arduino programming language (based on Wiring), and the Arduino Software (IDE), based on Processing.
Pin Diagram of DHT22 Sensor
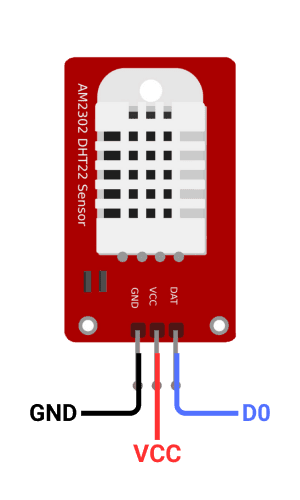
Circuit Diagram
Steps
1. Connect VCC to 5V, GND to GND.
2. Connect data pin to digital pin.
3. Install DHT library in Arduino IDE.
4. Write code to read sensor data.
5. Initialize sensor in setup().
6. Read temperature and humidity in loop().
Code
1
2#include <DHT.h>
3
4// Define the DHT11 sensor type and the pin where it is connected
5#define DHTPIN 7 // DHT11 data pin connected to pin 7
6#define DHTTYPE DHT11 // DHT 11 sensor
7
8DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE); // Initialize the DHT sensor
9
10void setup() {
11 // Start the serial communication for output
12 Serial.begin(9600);
13
14 // Initialize the DHT sensor
15 dht.begin();
16}
17
18void loop() {
19 // Wait a few seconds between measurements
20 delay(2000);
21
22 // Reading temperature and humidity from DHT11
23 float humidity = dht.readHumidity();
24 float temperature = dht.readTemperature(); // In Celsius
25 // If you want Fahrenheit, use dht.readTemperature(true);
26
27 // Check if any read failed and exit the function early
28 if (isnan(humidity) || isnan(temperature)) {
29 Serial.println("Failed to read from DHT sensor!");
30 return;
31 }
32
33 // Print the results to the Serial Monitor
34 Serial.print("Humidity: ");
35 Serial.print(humidity);
36 Serial.print(" % ");
37 Serial.print("Temperature: ");
38 Serial.print(temperature);
39 Serial.println(" *C");
40}
41
42